Empires have played a crucial role in shaping the modern world, influencing culture, politics, and economics across the globe. This blog post explores ten great empires that have left an indelible mark on history, contributing to the development of contemporary society. From ancient civilizations to more recent powers, these empires showcase the diverse ways in which human societies have organized themselves and interacted with one another.
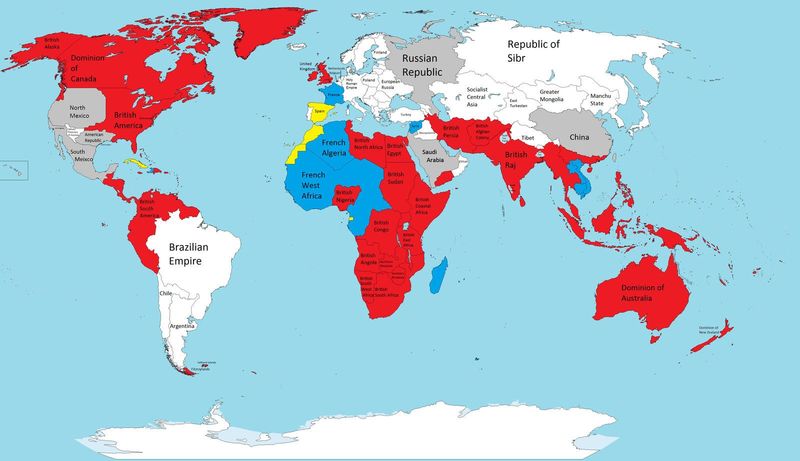
The Roman Empire
The Roman Empire, stretching from Britain to Egypt, was one of the most influential empires in history. Its legal system laid the foundation for modern law. Roman architecture, like the Colosseum, inspires awe even today.
The Empire fostered the spread of Christianity, significantly impacting religious history. Rome’s expansive roads facilitated trade and cultural exchange across Europe and beyond.
Although the Western Roman Empire fell in 476 AD, its legacies, including the Latin language and Roman numerals, endure. The Eastern Roman Empire, or Byzantine Empire, continued Rome’s legacy until 1453.
The British Empire
At its height, the British Empire was the largest in history, spanning continents and impacting millions of lives. The English language spread worldwide, becoming a global lingua franca.
British colonies saw the introduction of parliamentary systems, influencing governance structures. The empire’s trade networks facilitated the global spread of goods and ideas.
However, its legacy is complex, with discussions on colonialism’s moral implications continuing. Despite its dissolution, the Commonwealth of Nations maintains cultural and political ties among former colonies, reflecting the enduring impact of British governance.
The Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, a formidable power from the 14th to early 20th centuries, was a bridge between Eastern and Western cultures. Renowned for its architectural marvels, like the Hagia Sophia, the empire was a hub of Islamic arts and sciences.
The Ottomans controlled vital trade routes, fostering economic prosperity and cultural exchanges. Their legal system, the Millet, allowed religious communities autonomy, a precursor to modern multicultural policies.
Despite its eventual decline after World War I, the cultural and architectural legacies of the Ottoman Empire remain influential, particularly in its successor state, Turkey.
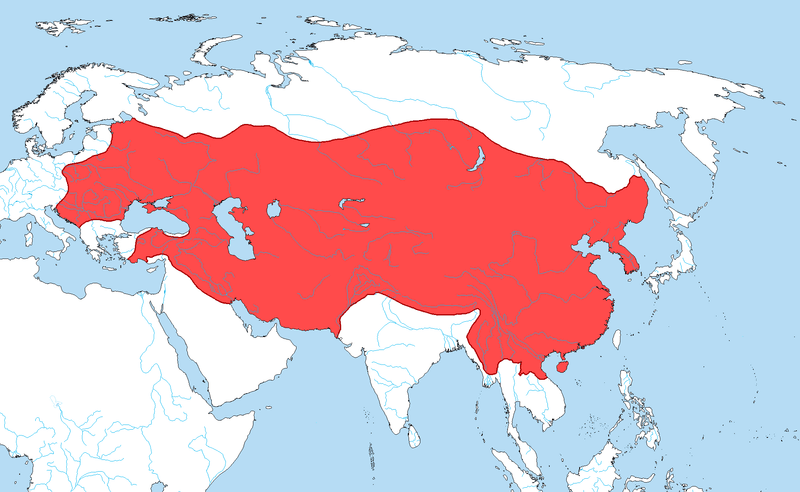
The Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire, led by Genghis Khan, was the largest contiguous empire in history. Known for its formidable cavalry, it united much of Asia under a single rule, promoting trade and communication.
The Pax Mongolica, or Mongol Peace, allowed for safer trade routes like the Silk Road, enhancing cultural and economic interactions. Mongol governance was surprisingly meritocratic, valuing skills over aristocratic lineage.
Although the empire eventually fragmented, it left a lasting impact on Eurasian history, facilitating exchanges between East and West, and influencing military strategies and administrative practices.
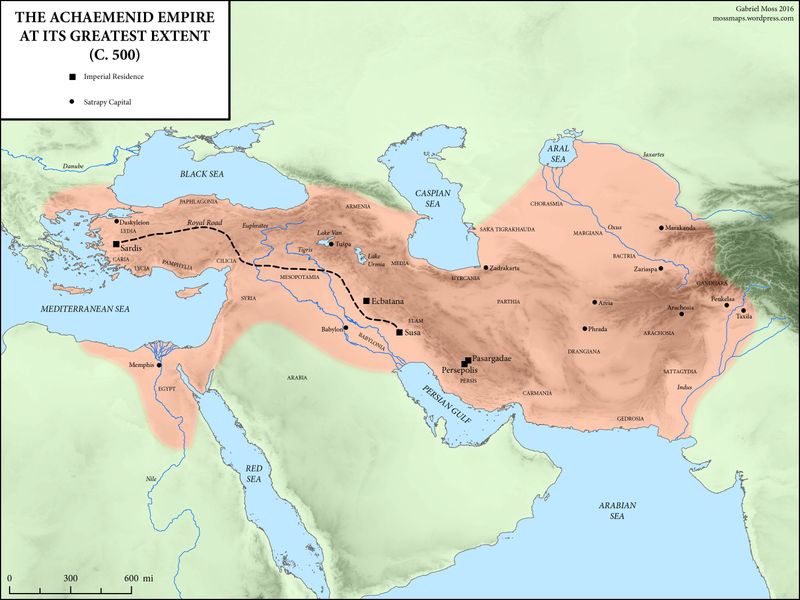
The Persian Empire
The Persian Empire, under Cyrus the Great, was a beacon of innovation and governance, spanning three continents. Known for its sophisticated bureaucracy and infrastructure, it set precedents in administration and communication.
The Royal Road facilitated efficient governance and trade, enhancing the empire’s cohesion. Persians were also pioneers in human rights, with the Cyrus Cylinder often cited as an early declaration.
The empire’s fall to Alexander the Great did not erase its influence. Persian culture, art, and political systems have continued to inspire and shape civilizations throughout history.
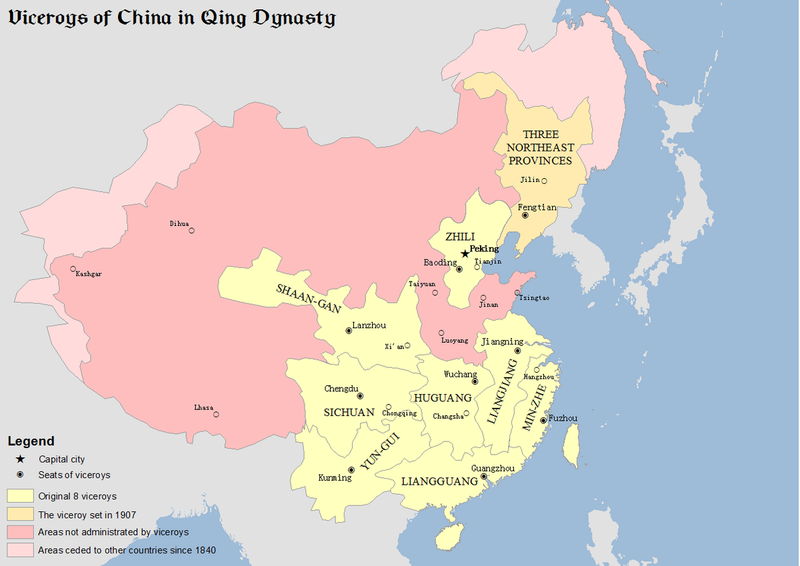
The Chinese Empire
The Chinese Empire, with its dynastic cycles, has been a pillar of culture and innovation. The Han Dynasty saw unprecedented advancements in technology, trade, and arts.
The Great Wall and the Silk Road are testaments to China’s ability to fortify and connect its vast territories. Confucian philosophy, which flourished during these times, continues to influence East Asian societies.
Despite periods of fragmentation, China’s imperial legacy endures, evident in its rich cultural traditions and contributions to global civilization. Modern China continues to draw from its imperial past, balancing tradition and progress.
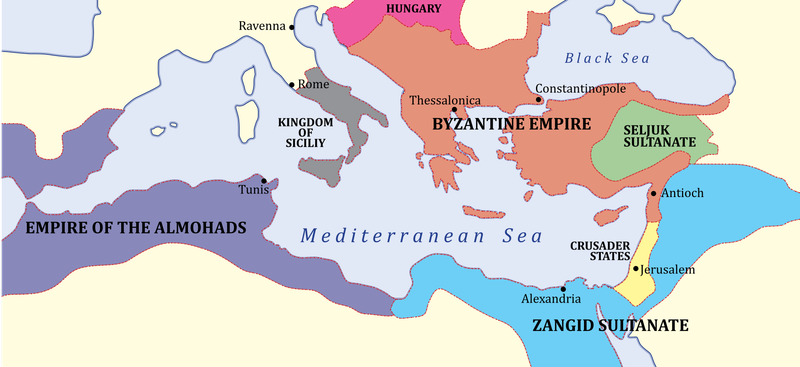
The Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, the eastern continuation of the Roman Empire, was a bastion of Christian culture and Hellenistic traditions. Its capital, Constantinople, was a hub of trade and culture.
Under Emperor Justinian I, the empire saw the codification of Roman laws, influencing legal systems worldwide. The Hagia Sophia, an architectural marvel, epitomizes Byzantine artistic achievements.
Although it fell to the Ottoman Turks in 1453, Byzantine influence persists in Orthodox Christianity and art. The empire’s blending of Greek, Roman, and Christian elements enriched civilizations, leaving a profound legacy in Eastern Europe.
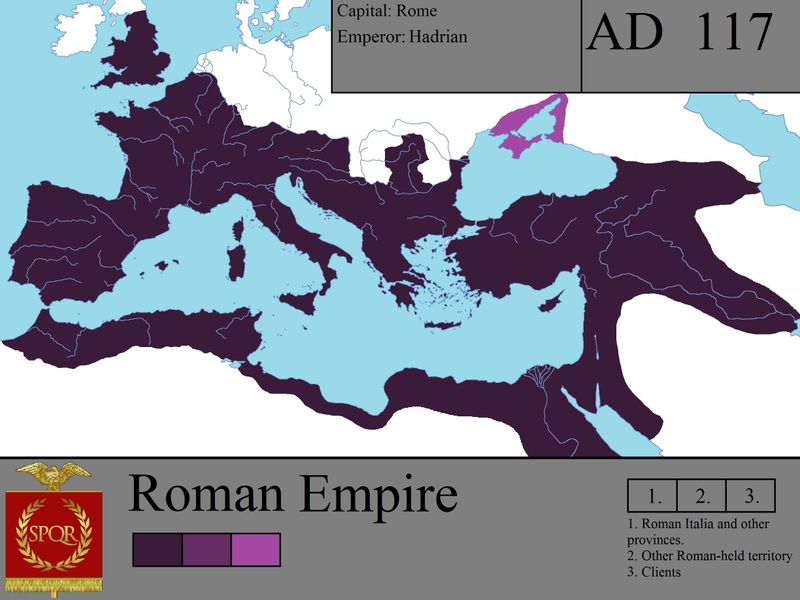
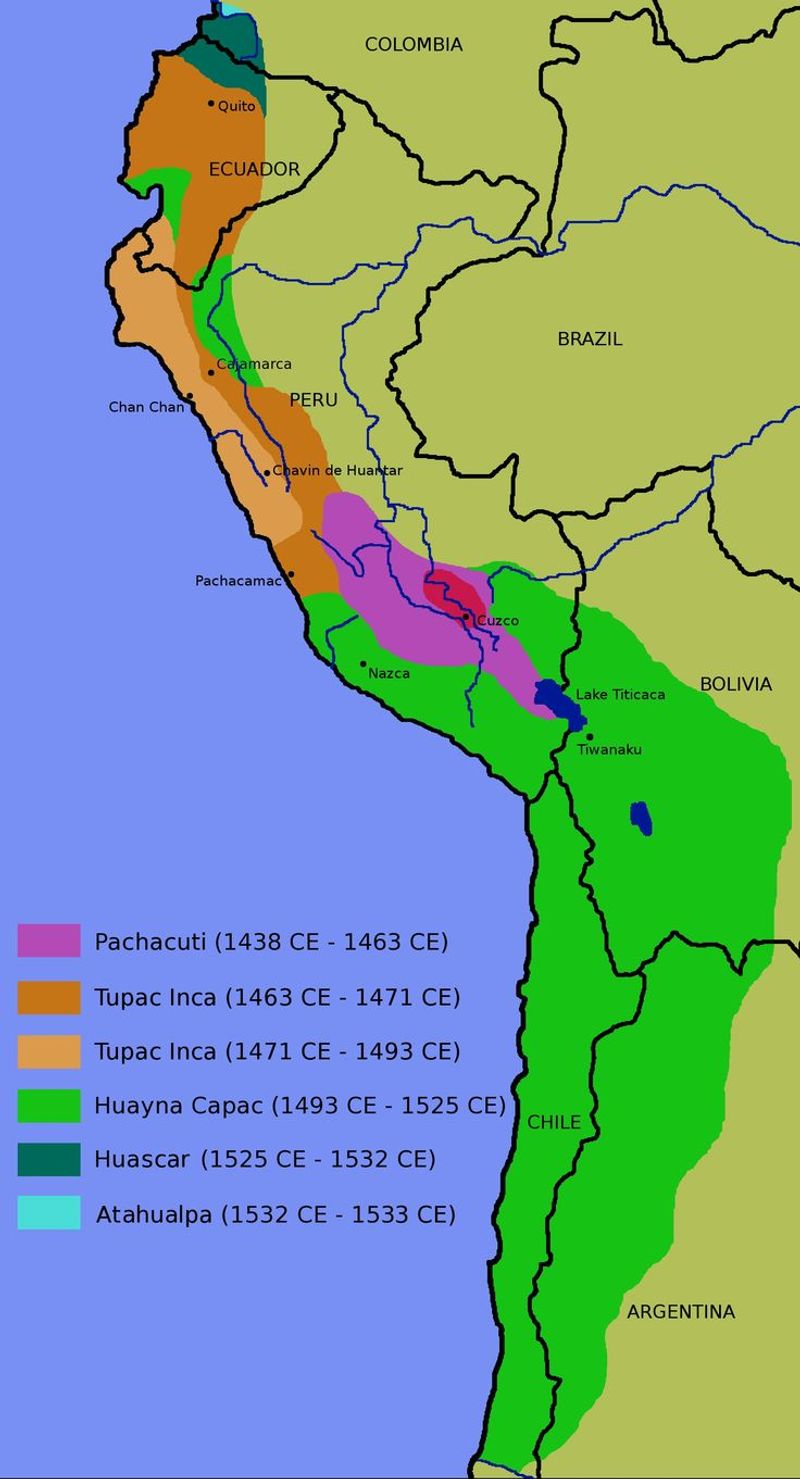
The Inca Empire
The Inca Empire, nestled in the Andes, was a marvel of organization and engineering. Known for its complex road systems, the Incas connected diverse regions, facilitating trade and communication.
Machu Picchu, a symbol of Incan architectural ingenuity, attracts millions today. The empire’s agricultural terraces demonstrate advanced farming techniques, sustaining large populations.
Despite Spanish conquest, Incan cultural and technological legacies persist in South America. The Quechua language and traditions continue to thrive, illustrating the enduring impact of the Inca civilization on the Andean region and beyond.
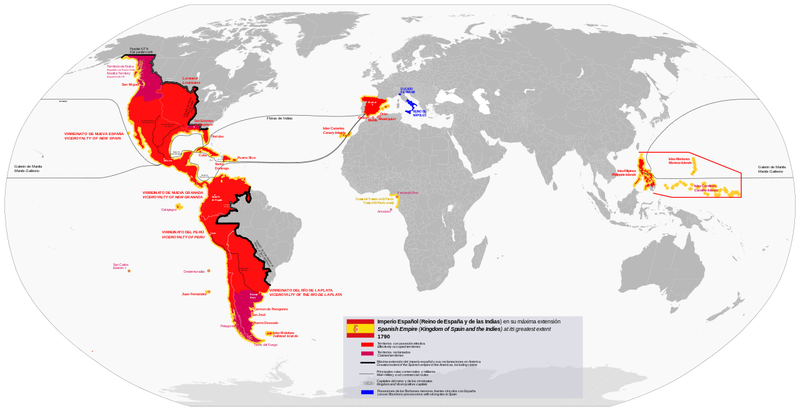
The Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire was a pioneer in European exploration and colonization, with vast territories in the Americas, Asia, and Africa. Its maritime prowess enabled the spread of Christianity and European culture.
The empire’s influence reshaped global trade, with the establishment of routes linking the Old and New Worlds. Spanish art and architecture flourished, leaving a rich cultural legacy.
Despite its decline, the Spanish language and culture endure, influencing societies worldwide. The empire’s history is complex, marked by both achievements and controversies, reflecting the multifaceted nature of imperial legacy.
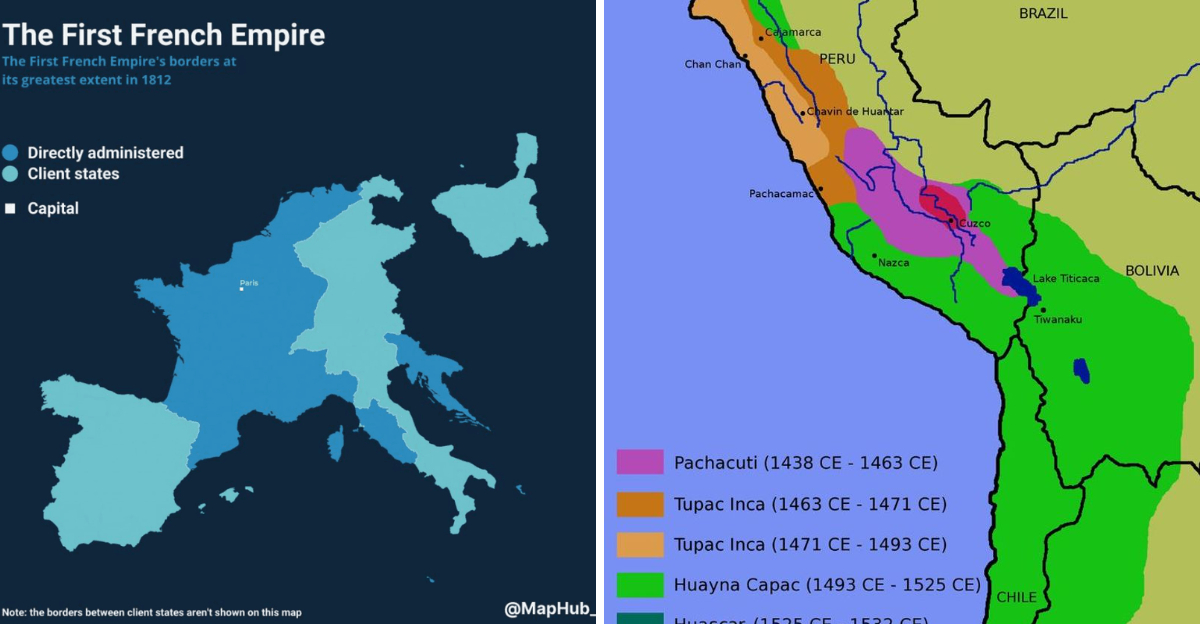
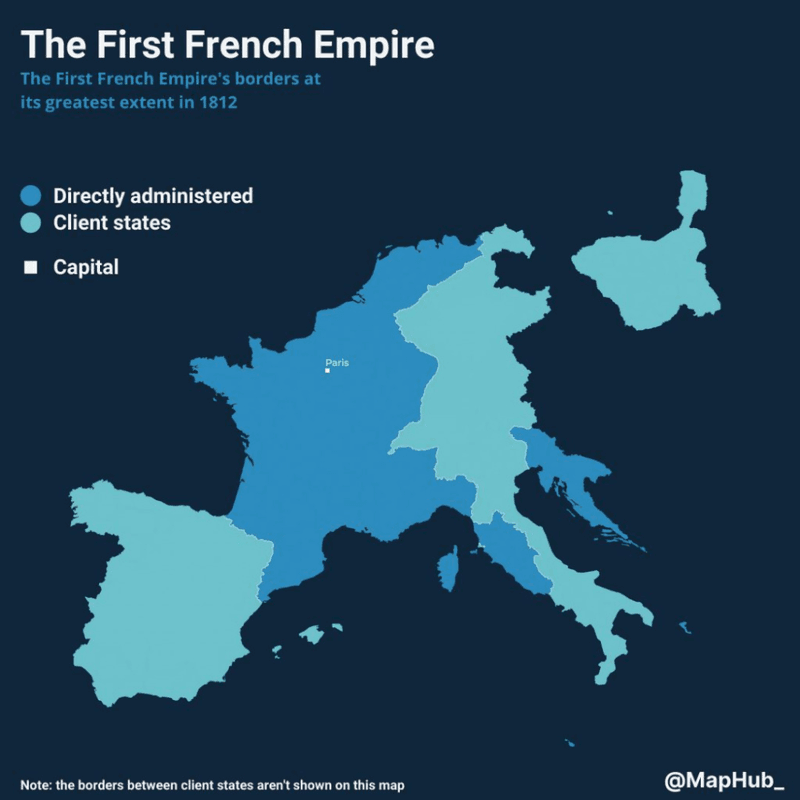
The French Empire
The French Empire, particularly under Napoleon Bonaparte, reshaped Europe through the Napoleonic Wars. Its influence extended globally, with colonies in Africa, Asia, and the Americas.
French legal codes, like the Napoleonic Code, impacted legal systems worldwide. The empire’s cultural contributions, from cuisine to fashion, enhanced global arts and sciences.
Although the empire eventually waned, France’s cultural and political influence persists. The French language and culture remain integral to global discourse, illustrating the lasting impact of France’s imperial endeavors on the world stage.